 |
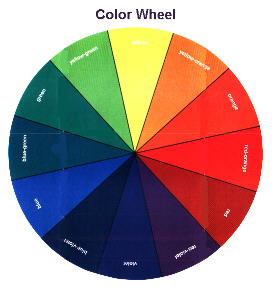
| Color has three qualities - hue, value, and intensity. Hue is the name of a color, such as yellow, red, or green. "Value" is the lightness or darkness of a hue. A "tint" is a hue plus white. A "shade" is a hue plus black. A "tone" is a hue plus gray. "Intensity" is the brightness or dullness of a hue. The term "warm" refers to warm hues on the color wheel, such as yellow, orange, and red combinations. The term "cool" refers to cold hues on the color wheel, such as green, blue, and violet combinations. |
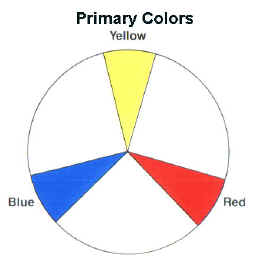 |
| Primary colors are red, yellow, and blue and cannot be made by combining any other colors. |
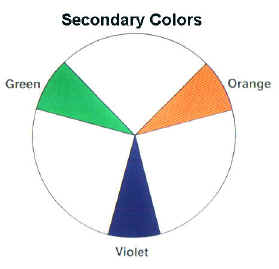 |
| Secondary colors are derived by combining two primary colors. Green is made of blue and yellow. Orange is made of red and yellow. Violet is made of blue and red. |
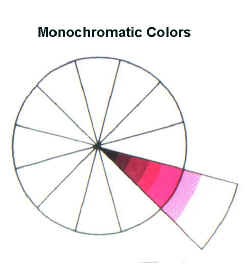 |
| Monochromatic colors schemes are made up of one hue with various values and intensities of that one hue. |
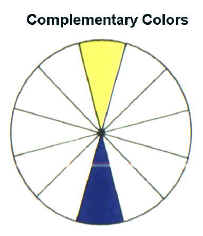 |
| Complementary color schemes are made up of two hues directly opposite each other on the color wheel. For example, yellow and violet or red and green or blue and orange. These combinations have the strongest contrast. |
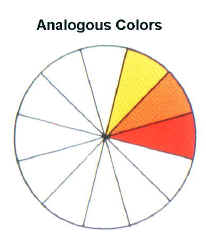 |
| Analogous color schemes are a combination of three colors directly next to each other on the color wheel with one hue in common. For example, yellow-orange, orange, and red-orange have orange in common. |
copyright © 1997 - 2024, Fiber Images™. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.